A survey of chemical and biological products used in intensive prawn farms in the Philippines
- Global styles
- MLA
- Vancouver
- Elsevier - Harvard
- APA
- Help

View/
Date
1993Page views
4,525ASFA keyword
AGROVOC keyword
Taxonomic term
Metadata
Show full item record
Share
Abstract
With attractive prawn export prices and the availability of hatchery fry and commercial feeds, Philippine aquaculture has experienced a shift from milkfish to prawn Penaeus monodon and an intensification from traditional and extensive prawn culture to higher stocking densities. This paper features the results of a survey of intensive prawn farms (n = 21) in Western Visayas and Northern Mindanao conducted in 1990. Average farm size, production, feeding and water management are described. To solve the self-pollution characteristic of intensive ponds, the farms utilized some 40 chemical and biological products; at least another 35 were available in the market at the time of the study. These include therapeutants and disinfectants, soil conditioners, bacteria-enzyme preparations, algicides and piscicides, plankton growth promoters, and feed additives. The possible ecological effects of effluents drained into adjacent marine waters are discussed; some recommendations are given.
Suggested Citation
Primavera, J., Lavilla-Pitogo, C. R., Ladja, J. M., & de la Peña, M. R. (1993). A survey of chemical and biological products used in intensive prawn farms in the Philippines. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 26(1), 35-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(93)90595-B
Type
ArticleISSN
0025-326XCollections
- Journal Articles [1262]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
Water quality in Imbang river, Negros Occidental: effluents and pollutant loads from agriculture, sugar mills, households, and shrimp farms
Gonzales, Guadiosa A.; Gonzales, Hernane J.; Sanares, Roman C.; Taberna, Evelyn T. (Bureau of Agricultural Research, Department of Agriculture, 2007)An ecological assessment of Imbang River in Negros Occidental was undertaken from December 1992 to February 1995. The effluents from sugar mills, households, shrimp farms, sugarcane plantations and rice fields were ... -
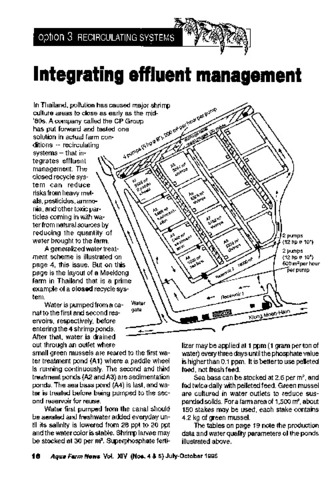
Integrating effluent management
Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1996)The paper discusses a closed recycle shrimp farm in Thailand which integrates effluent management. The closed recycle system can reduce risk of heavy metals, pesticides, ammonia, and other toxic particles coming in with ... -
From triphenyltins to integrated management of the 'pest' snail Cerithidea cingulata in mangrove-derived milkfish ponds in the Philippines
The potamidid snail Cerithidea cingulata is considered a pest in brackishwater milkfish ponds in the Philippines and has been controlled by the triphenyltin (TPT) compounds Aquatin and Brestan. But TPT is also toxic to ...