Elemental sulfur in the gills of the mangrove mud clam Anodontia edentula (Family Lucinidae)
- Global styles
- MLA
- Vancouver
- Elsevier - Harvard
- APA
- Help

ดู/
วันที่
2000ผู้เขียน
Page views
2,087ASFA keyword
AGROVOC keyword
Taxonomic term
Geographic names
เมตาดาต้า
แสดงระเบียนรายการเต็ม
Share
นามธรรม
Different sizes of the mangrove mud clam Anodontia edentula were collected from the mangroves in Brgy. San Roque in Estancia, Iloilo, central Philippines, and the mantle, gill, and foot tissues were analyzed for elemental sulfur content. Mangrove mud (substrate) was also analyzed for total sulfur content to establish the possibility of clam-bacteria symbiosis in this lucinid clam. Sulfur analysis showed highly significant (p <0.0001) amounts of elemental sulfur in the gills (247.64 ± 63.28 μmoles/g FW) compared with the quantities observed in the mantle (0.84 ± 0.22 μmoles/g FW). Elemental sulfur was absent from the foot tissues. Results also showed a significantly (p <0.05) decreasing elemental sulfur from the newly collected clams (mean = 461.18 μmoles/g FW) compared to those reared in the laboratory (mean = 159.08 μmoles/g FW: with mangrove mud substrate; mean = 45.18 μmoles/g FW without substrate), which were analyzed weekly until week 3, indicating that stored elemental sulfur is being utilized by the bacteria in the absence of sulfide. Total sulfur content of mangrove mud in situ was higher than that used us substrate in the experiment; where there were no significant differences from initial to final readings. This shows that mangrove mud in situ is linked to a steady sulfur source.
Keywords
Toothless platter shell mangrove mud clam Anodontia edentula lucinid gills elemental sulfur imbao mangrove clamการอ้างอิง
Lebata, J. H. L. (2000). Elemental sulfur in the gills of the mangrove mud clam Anodontia edentula (Family Lucinidae). Journal of Shellfish Research , 19(1), 241-245. http://hdl.handle.net/10862/1857
Type
ArticleISSN
0730-8000คอลเลกชัน
- Journal Articles [1261]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
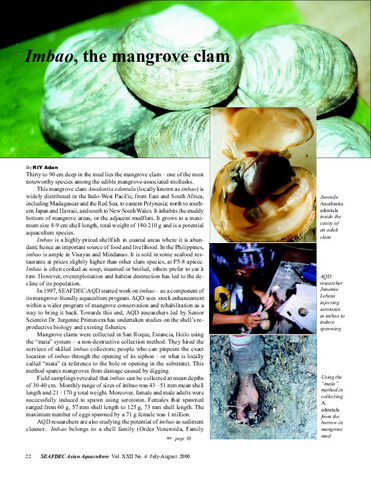
Imbao, the mangrove clam
Adan, R. I. Y. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 2000) -
Collection of the clam Anodontia edentula in mangrove habitats in Panay and Guimaras, central Philippines
Primavera, Jurgenne ; Lebata, M. J. H. L.
; Lebata, M. J. H. L.  ; Gustilo, Lillian F.; Altamirano, Jon
; Gustilo, Lillian F.; Altamirano, Jon  (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002)
The mangrove clam Anodontia edentula is highly prized in the Philippines for its flavor and large size. Because this infaunal species is found down to one meter deep in mangrove areas, harvesting the clam reportedly damages ...
(Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002)
The mangrove clam Anodontia edentula is highly prized in the Philippines for its flavor and large size. Because this infaunal species is found down to one meter deep in mangrove areas, harvesting the clam reportedly damages ... -
Oxygen, sulphide and nutrient uptake of the mangrove mud clam Anodontia edentula (Family: Lucinidae)
Oxygen, sulphide and nutrient (ammonia, nitrite and phosphate) uptake of Anodontia edentula was measured. Oxygen and sulphide were measured from sealed containers provided with 1 l fresh mangrove mud (sulphide source) and ...