Giant freshwater prawn culture in Indonesia
- Global styles
- MLA
- Vancouver
- Elsevier - Harvard
- APA
- Help
Share
抄録
Indonesia is one of the countries in Asia with rich biodiversity, particularly in terms of the number of endemic freshwater aquatic organisms. Numerous indigenous freshwater fish species are found in Sumatera (30 spp.), Kalimantan (149 spp.), Java (12 spp.), and in Sulawesi (52 spp.) (Anonymous, 1994; Kottelat et al., 1993). These fauna are distributed in a total of 55 million hectares of freshwater resources consisting of lakes, dams, swamps, etc. The potential area for freshwater fish pond culture is estimated at 233,124 ha with a production of 334,085 mt/year (DGF, Indonesia. 2001), of which about 5,140 metric tons come from giant freshwater prawn culture.
Freshwater prawns are farmed in West Java, i.e., in Ciamis (Tambaksari, Pamarican and Kalipucang) and Tasikmalaya. Government- and privately-owned commercial hatcheries are mostly found in Jogjakarta. In East Java, Macrobrachium culture is done in brackishwater ponds. Freshwater prawn culture has also spread to Bali Island, e.g., Gianyar, Klungkung, Buleleng and Tabanan.
Indonesia is recognized as the center of origin of freshwater prawns and to date, there are about 19 species found in its natural waters (Holthuis, 1980). Despite the advanced development of freshwater prawn culture and the availability of natural prawn populations in Indonesia, slow prawn growth rate, diseases and small edible portion remain unsolved. In recent years, the Indonesian Government through its fisheries research agency, has focused on improving the commercial production of the freshwater prawn through genetic means. Thus in 2001, a genetically improved stock of freshwater prawn has been developed and released for culture to local prawn farmers. This stock or strain has been referred to as the GI Macro or the Genetically Improved Macrobrachium rosenbergii.
Suggested Citation
Nugroho, E., & Emmawati, L. (2007). Giant freshwater prawn culture in Indonesia. In M. R. R. Eguia & M. L. C. Aralar (Comp.), Recent developments in the genetic improvement of the giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium sp.) (pp. 4–7). Tigbauan, Iloilo, Philippines: Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center.
Type
Book chapterISBN
9789718511848
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
The Philippine aquaculture industry
Camacho, Arsenio S.; Macalincag-Lagua, Natividad (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1988)The aquaculture sector of the Philippine fishing industry registered the highest growth rate of 12.5% in 1977-1986. The contribution of aquaculture to the total fish production was equivalent to 24% in 1986 compared to ... -
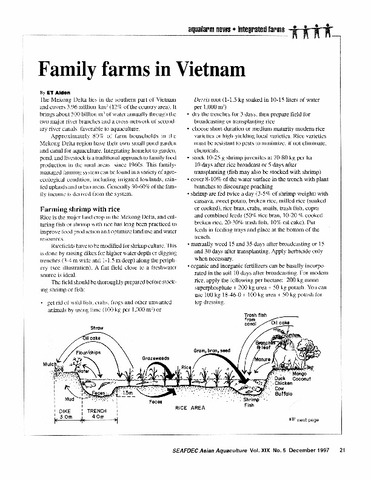
Family farms in Vietnam
Aldon, Eva T. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1997) -
Nursery and grow-out operation and management of Penaeus monodon (Fabricius)
Corre, Kaylin G. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1988)The results of research on nursery and grow-out rearing of prawn conducted by the SEAFDEC Aquaculture Department for over a decade are reviewed. Different rearing facilities designed to accommodate hatchery-produced prawn ...