Transformation of Laguna Lake from a marine arm of Manila Bay to a freshwater system
- Global styles
- MLA
- Vancouver
- Elsevier - Harvard
- APA
- Help
Share
นามธรรม
Evolution of Laguna Lake during the past 6,000 years is established using paleontologic, sedimentologic, and geochemical profiles of a 10.5-meter long sediment core from the western lobe. Marine molluscan and diatom assemblages reveal a lagoonal environment with depths initially greater than 10 m, 5,700 radiocarbon years ago (yBP), then it consistently shallowed to intertidal depths until 3,700 yBP. Tellina sp., Leptaxinus sp., and Anomalocardia sp. predominated the molluscan fauna. The marine Cyclotella stylorum, Thalassiosira eccentrica, and Thalassiosira lineata, comprise 80% of the diatom fauna.
Brackish water condition was short-lived and it was succeeded by freshwater conditions set at the appearance of Vivipara burroughiana 3,000 yBP. The XRF-derived sulfur, strontium, and calcium concentrations and their aluminum-normalized trends used as geochemical proxy records, corroborate the changing salinity levels and the age boundaries set from the molluscs.
Lowering of sea level from the mid Holocene high and vertical movements across the West Marikina Valley Fault, which presently bound the western edge of Laguna Lake, led to the emergence of the Muntinlupa-Paranaque stretch, isolating the proto-Laguna Lake from Manila Bay. Pulsed decreases of salinity to freshwater levels at 250-year intervals and the associated emergence of a 30 m-high barrier reveal a large tectonic influence as opposed to small climatic and sea level shifts within this period. In the last few decades, a new phase of environmental shift has been occurring in the lake. Global warming and land subsidence elevated the saltwater backflow into the lake, enough to leave an increasing salinity trend in the sediment record.
Description
Abstract only.
การอ้างอิง
Jaraula, C. B., & Siringan, F. P. (2005). Transformation of Laguna Lake from a marine arm of Manila Bay to a freshwater system. In M. L. Cuvin-Aralar, R. S. Punongbayan, A. Santos-Borja, L. V. Castillo, E. V. Manalili, & M. M. Mendoza (Eds.), Proceedings of the First National Congress on Philippine Lakes (p. 124). Southeast Asian Regional Center for Graduate Study and Research in Agriculture (SEARCA).
Type
Conference paperISSN
1656-8099คอลเลกชัน
- LakeCon2003 [49]
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
An environmental assessment of the aquaculture potential of Lake Gawaan, Lake Lenneng and Lake Banao/Danum at the Mt. Province
Dang-awan, Rebecca G.; Estima, Martha; Gayagay, Petra; Pagtan, Aida; Ramos, Ma. Abegail A. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center; Philippine Council for Aquatic and Marine Research and Development (PCAMRD), Department of Science and Technology; Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, 2001)This study reviews the existing conditions of the three Mt. Province lakes: Lake Gawaan, Lake Lenneng and Lake Banao/Danum. Three mechanisms were employed. First is the overview of the resource capabilities. This includes ... -
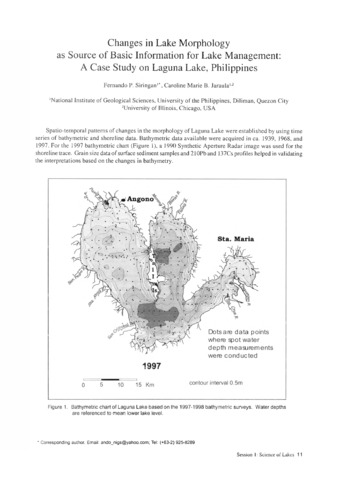
Changes in lake morphology as source of basic information for lake management: A case study on Laguna Lake, Philippines
Siringan, Fernando P.; Jaraula, Caroline Marie B. (Southeast Asian Regional Center for Graduate Study and Research in Agriculture (SEARCA), 2005) -
Assessment of local government's implementation of open access policy in Taal Lake, Philippines: Effects on lake conservation and management
Mercene-Mutia, Ma. Theresa (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center; Philippine Council for Aquatic and Marine Research and Development (PCAMRD), Department of Science and Technology; Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, 2001)The effects of local government's implementation of the current national policy on open access in municipal fisheries are assessed in terms of their impact on the fishery resources of Taal Lake. Local officials and fisherfolk ...