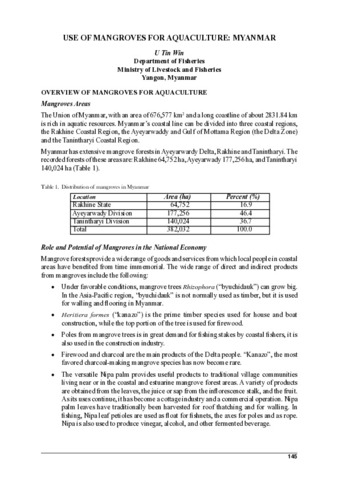
Use of mangroves for aquaculture: Myanmar.
- Global styles
- MLA
- Vancouver
- Elsevier - Harvard
- APA
- Help
Share
Abstract
Aquaculture has only started to develop rapidly in the past few decades, due to better knowledge of culture species, improved methodologies and techniques in breeding, nutrition and increasing demand for food fish of high-value species such as shrimps, sea bass and groupers.
Mangrove deforestation has an impact on shrimp culture itself, the success of the latter (when traditional culture method is used) depends on stocking of wild fry. For semi-intensive and intensive shrimp culture, the number of wild caught spawners may decrease because wild shrimp populations also use mangrove swamps as its feeding ground.
Other negative effects of mangrove destruction to make way to shrimp ponds, include water pollution from pond effluents, sedimentation from the release of solid materials from pond, interruption of the tidal water flow, dwindling natural shrimp and fish stock due to increased pollution or product contamination due to indiscriminate use of chemicals.
Chemicals and drugs (antibiotic) should not be used in fish and shrimp culture for prevention and control of bacteria and viral diseases. In order to ensure the sustainable development of aquaculture, it is important to bear in mind the interdependence of technology and natural resource under various socioeconomic setting.
Suggested Citation
Win, U.T. (2004). Use of mangroves for aquaculture: Myanmar. In: Promotion of mangrove-friendly shrimp aquaculture in Southeast Asia (pp. 145-150). Tigbauan, Iloilo, Philippines: Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center.
Type
Meeting reportCollections