The status of tilapia aquaculture in Lake Sebu, South Cotabato
- Global styles
- MLA
- Vancouver
- Elsevier - Harvard
- APA
- Help
Share
Abstract
Tilapia culture in Lake Sebu started in the early 1970's and is now considered the backbone of the economy and major driving force of the development of the Municipality of Lake Sebu. About 19% of Lake Sebu's 354 ha water area is used for aquaculture. The present tilapia production system is not as intensive as in other lakes in the country. The daily 3-ton tilapia harvest is marketed in the different towns within the province and in neighboring provinces. Municipal Ordinance 01, Series of 1994 regulates fish cage establishment within the lake. The local government unit launched a semi-annual 'Oplan Linis', a clean up operation to remove floating debris, water hyacinth, and other vegetation along the lakeshore. Reforestation has been implemented as part of the watershed management program. For centralized marketing and effective collection of revenues, a fish port was opened in January 1997. The tilapia industry in Lake Sebu is now confronted with several setbacks. Poor-quality seeds require a longer culture period and, despite higher inputs, still result in low production. Fish kills, locally termed 'kamahong', are becoming more frequent and devastating. Market competition is another problem. Producers of intensively fed tilapia from Lake Sebu have to contend with a large volume of unfed and low priced tilapia from Lake Buluan (Lutayan area).
Suggested Citation
Beniga Z. M. (2001). The status of tilapia aquaculture in Lake Sebu, South Cotabato. In C. B. Santiago, M. L. Cuvin-Aralar, & Z. U. Basiao (Eds.), Conservation and Ecological Management of Philippine Lakes in Relation to Fisheries and Aquaculture (pp. 95-98). Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Aquaculture Department, lloilo, Philippines; Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: Philippine Council for Aquatic and Marine Research and Development (PCAMRD), Department of Science and Technology; Quezon City, Philippines: Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR), Department of Agriculture, Quezon City, Philippines.
Type
Conference paperISBN
9718511539
Related items
Showing items related by title, author, creator and subject.
-
The Philippine aquaculture industry
Camacho, Arsenio S.; Macalincag-Lagua, Natividad (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1988)The aquaculture sector of the Philippine fishing industry registered the highest growth rate of 12.5% in 1977-1986. The contribution of aquaculture to the total fish production was equivalent to 24% in 1986 compared to ... -
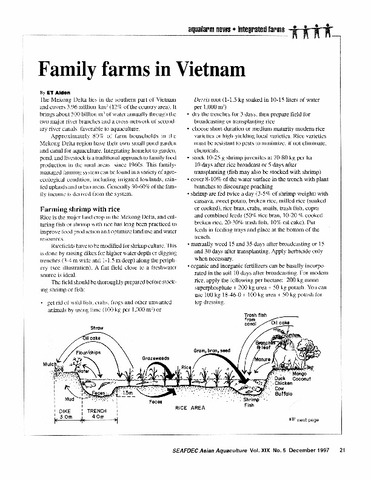
Family farms in Vietnam
Aldon, Eva T. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1997) -
Nursery and grow-out operation and management of Penaeus monodon (Fabricius)
Corre, Kaylin G. (Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, 1988)The results of research on nursery and grow-out rearing of prawn conducted by the SEAFDEC Aquaculture Department for over a decade are reviewed. Different rearing facilities designed to accommodate hatchery-produced prawn ...